Event
- 10 Aug 2020 08:56:15 PDT, (33.247, -115.682), depth 10.8km.
- 12km SSE of Bombay Beach, California
Aftershocks
- As of 10 Aug 2020, 10:16AM PDT, there have been 29 aftershocks recorded.
- The largest was M4.0 (smallest M1.3).
- More aftershocks may be expected in the next few days, the largest expected is approximately 1 magnitude unit smaller than the mainshock.
- There is a small chance (about 5%) that a larger quake could occur, with the likelihood decreasing over time.
Possible Foreshocks
- There were 6 events during the 3 days prior to the earthquake (within a 10 km radius).
- The largest was M3.5 (2020/08/10).
Historical Seismicity
- Since our records began in 1932 we’ve had 50 events of M4 or greater within 10km of today’s event.
- The largest historic event was M5.8 on 1945/08/15.
- The most recent historic event was M4.1 on 27 Sep 2016.
- m4.8 2009/03/21
- m4.3 2016/09/26
Faults
- CFM fault association: Most Likely Elmore Ranch fault (68%).*
- Nearby faults: Brawley Seismic Zone faults, , San Andreas fault zone, Coachella section (12.0 km) and Hot Springs fault (14.2 km).**
Additional Information
- Links for: USGS earthquake page, ShakeMap, DYFI, waveforms.
- Visit our special reports page for further information on local notable earthquakes.
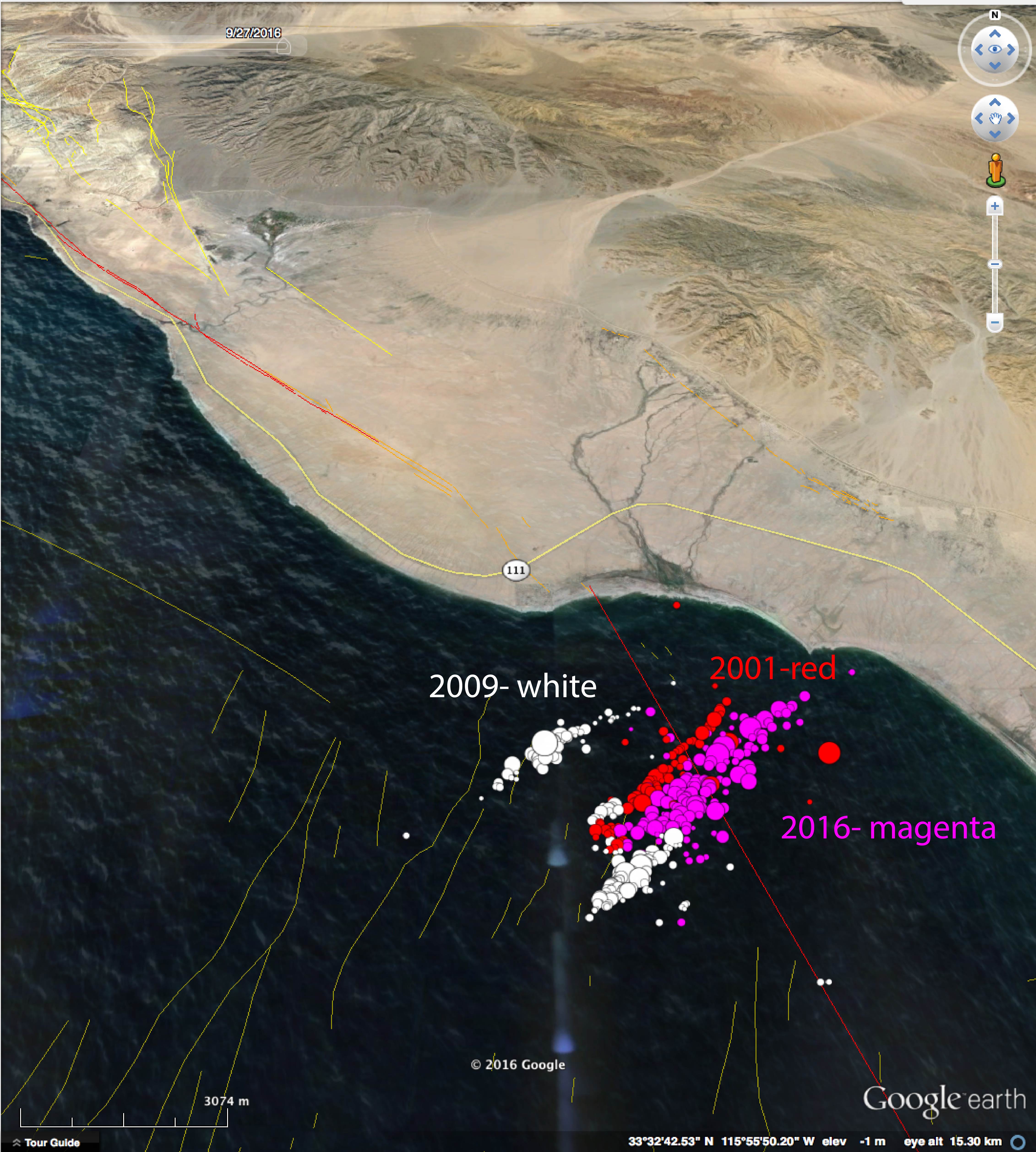
The events in this sequence are occurring to the south of the 2016, 2009, and 2001 events shown here. Updated graphics will be replaced once available.
Below are the waveform data associated with this event, as recorded in our Live Seismograms Feed.
*Earthquakes can occur both near or on major known faults, and in places where no clear fault zones are known. Using the statistical method of Evans et al. (in prep. 2019) the location and focal mechanism of this earthquake suggest the above association with modeled faults in the Community Fault Model (CFM) provided by the Southern California Earthquake Center (SCEC) and Harvard University. Note that the CFM fault association may be different from the nearby faults list. Differences may arise due to different fault databases, and because the CFM fault association uses the hypocenter with relation to subsurface 3-dimensional fault orientation models, while the nearby faults list utilizes mapped surface traces as they relate to the epicenter.
CFM Fault: SCEC CFM 5.0 Fault name and closest segment if available; The CFM is maintained by Harvard University, Dept of Earth & Planetary Sciences.
Probability: The probability in percent the earthquake is associated with this fault.
SCSN: Caltech/USGS Southern California Seismic Network
**U.S. Geological Survey and California Geological Survey, 2006, Quaternary fault and fold database for the United States, accessed 2015, from USGS web site: https://earthquake.usgs.gov/hazards/qfaults/
This information is subject to change as more up-to-date data become available.






